Understanding the Modern Data Stack: The Foundation of Enterprise Data Infrastructure
The modern data stack, or simply data stack, refers to a collection of cloud-native applications that form the backbone of an organization’s data infrastructure. In recent years, this concept has rapidly gained traction, becoming the go-to approach for companies of all sizes looking to derive meaningful insights from their data. Much like an industrial value chain, the modern data stack follows a clear process: data ingestion, transformation, storage, and productization.
In this article, we’ll introduce the core concepts of the modern data stack. Future posts will dive deeper into each of its components.
What is the Modern Data Stack?
The modern data stack is a combination of technologies designed to turn raw data into valuable business insights. By leveraging a variety of tools, this infrastructure simplifies the management of data platforms while ensuring maximum data utilization. Organizations can customize their data stack by choosing tools that align with their specific needs, adding layers and components based on use cases.
A Brief History of the Modern Data Stack
Initially, on-premise databases were sufficient for handling limited data storage needs. But as data volumes exploded, traditional databases struggled to keep up, leading to the development of new technologies like Hadoop, Vertica, and MongoDB in the early 2000s. This era, known as the Big Data era, introduced distributed SQL and NoSQL systems that allowed organizations to handle increasing data volumes.
However, the Big Data era gave way to the rise of cloud technologies in the early 2010s. Legacy on-premise systems couldn’t compete with the agility and scalability of cloud-based data warehouses like Amazon Redshift (launched in 2012), Google BigQuery, and Snowflake. These solutions fundamentally changed how companies approached data storage and management.
Key Developments That Enabled the Modern Data Stack
The current landscape of the modern data stack is the result of several key technological advancements. Here are some of the major changes that enabled its widespread adoption:
1. Cloud Data Warehouses
Amazon’s Redshift revolutionized the data warehousing landscape by introducing scalable, cloud-based solutions. Other cloud-native systems like BigQuery and Snowflake followed, ushering in a new era of data processing.
- Speed: Cloud data warehouses dramatically reduce query processing time, which was a major bottleneck in earlier systems.
- Connectivity: Connecting data sources to cloud data warehouses is more seamless compared to on-premise solutions.
- User Accessibility: Cloud data warehouses democratize data access, empowering more users within an organization.
- Scalability & Affordability: Cloud solutions are cost-effective and scalable, offering flexible pricing based on data volume and usage.
2. Shift from ETL to ELT
With traditional ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), data transformations happen before data is loaded into the warehouse. However, the shift to ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) allows organizations to load unstructured data first and apply transformations later. Cloud data storage made this possible by removing storage constraints and reducing pipeline costs.
3. Self-Service Analytics & Data Democratization
The rise of BI tools like Power BI, Looker, and Tableau has made data more accessible, enabling employees across organizations to leverage data for decision-making.
What Makes a Data Stack “Modern”?
It’s important to note that a cloud-based platform alone does not constitute a modern data stack. According to data experts, including Jordan Volz, modern data stacks must meet five key criteria:
- Centered around a cloud data warehouse
- Offered as a managed service with minimal setup effort
- Democratizes data access across the organization
- Supports elastic workloads
- Built with automation at its core
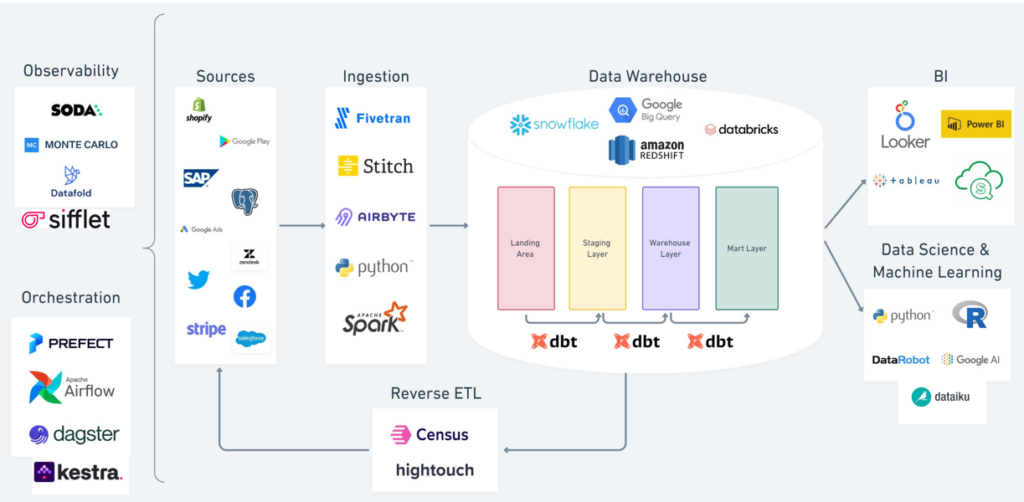
Components of the Modern Data Stack
Let’s explore the key technologies within the modern data stack. While each stack may differ, common components include:
1. Data Integration
- Main tools: Airbyte, Fivetran, Stitch
- Function: Data integration consolidates data from various systems (e.g., databases, CRM) into a central repository, like a data warehouse or data lake.
2. Data Transformation/Modeling
- Main tool: dbt
- Function: Transforming raw data into a structured format for analysis is critical. With cloud-based storage, most companies now use ELT, enabling transformations when necessary.
3. Workflow Orchestration
- Main tools: Airflow, Dagster
- Function: This involves scheduling and automating data pipelines to ensure data flows efficiently from source to destination.
4. Data Warehousing
- Main tools: Snowflake, Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift
- Function: The data warehouse serves as the central hub where data is stored, accessed, and analyzed.
5. Reverse ETL
- Main tools: Hightouch, Census
- Function: Reverse ETL moves data from the warehouse into external applications, enabling operational analytics and making data actionable for business teams.
6. BI & Analytics
- Main tools: Power BI, Looker, Tableau
- Function: BI tools allow organizations to analyze data and derive insights that drive business decisions.
7. Data Observability
- Function: Data observability tools ensure data reliability and monitor data quality throughout the pipeline, identifying issues before they affect business decisions.
Is There a Perfect Data Stack?
There’s no one-size-fits-all data stack. Every organization has different levels of data maturity, team structures, and specific needs. However, modern data stacks typically fall into three categories:
- Essential: Ingests, stores, and models data with basic BI tools like Metabase.
- Intermediate: Adds workflow orchestration and data observability to enhance monitoring and automation.
- Advanced: Incorporates more sophisticated tools for integration, transformation, and analytics, supporting large-scale data operations.
Conclusion
The modern data stack is transforming how organizations leverage data, making it more accessible, actionable, and scalable. By adopting the right combination of tools, companies can build a robust data infrastructure that enables real-time decision-making and future-proof business growth. As data ecosystems continue to evolve, so will the tools and technologies within the modern data stack, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with data. Stay tuned for deep dives into each component of the stack in upcoming articles!
